Personal loans are widely used for various financial needs, providing versatility and accessibility. Borrowers use personal loans for purposes like consolidating debts or covering unexpected expenses. These loans offer flexibility for individuals to address their financial requirements with ease.
Navigating personal finance raises the question of whether to prepay a personal loan.
This article provides insights into the dynamics of personal loans, starting with a brief overview of their nature and usage.
Repaying a personal loan ahead of schedule requires a nuanced evaluation of financial strategies and potential benefits.
Understanding Personal Loan Prepayment
What is loan repayment?
Loan prepayment is a financial strategy for repaying personal loans before the scheduled tenure ends. Personal loan pre approval and repayment entails making payments towards the principal amount of the loan ahead of the agreed-upon repayment schedule. This proactive approach can provide several potential advantages to borrowers.
Advantages include reducing overall interest payments on the loan. Borrowers may experience financial freedom sooner than originally expected by opting for loan prepayment.
How does personal loan prepayment work?
Personal loan prepayment involves allocating surplus funds towards settling the principal amount. Making additional payments beyond regular installments directly reduces the outstanding balance.
In summary, making additional payments beyond regular installments directly reduces the outstanding balance.
The surplus funds contribute to lowering the total interest payable on the remaining loan amount. This proactive approach can potentially result in long-term cost savings for borrowers.
The feasibility and implications of prepayment depend on the specific terms and conditions set by the lending institution.
Differentiating between full prepayment and partial prepayment
| Full Prepayment: | Partial Prepayment: |
| ● Full prepayment involves settling the entire outstanding loan amount in a single lump sum payment.
● Allows borrowers to clear their debt entirely. ● Eliminates monthly installments and interest obligations. ● Borrowers achieve financial freedom from the loan sooner than the originally scheduled tenure. ● Awareness of prepayment penalties or charges is crucial, as some lenders may impose fees. ● Lenders use these charges to compensate for the interest they would have earned over the entire loan tenure. ● Understanding associated fees is essential for borrowers considering full prepayment as a debt clearance strategy. |
● Partial prepayment entails making extra payments towards the loan without settling the entire outstanding balance.
● Borrowers can reduce the loan burden while maintaining the regular installment schedule. ● This approach provides a middle ground between repaying debt and adhering to the original repayment plan. ● Similar to full prepayment, borrowers should be vigilant about any associated charges or conditions imposed by the lending institution. ● Some lenders may limit the frequency or amount of partial prepayments. ● Understanding terms and conditions is crucial before opting for partial prepayment as a debt management strategy.
|
Advantages of Personal Loan Prepayment
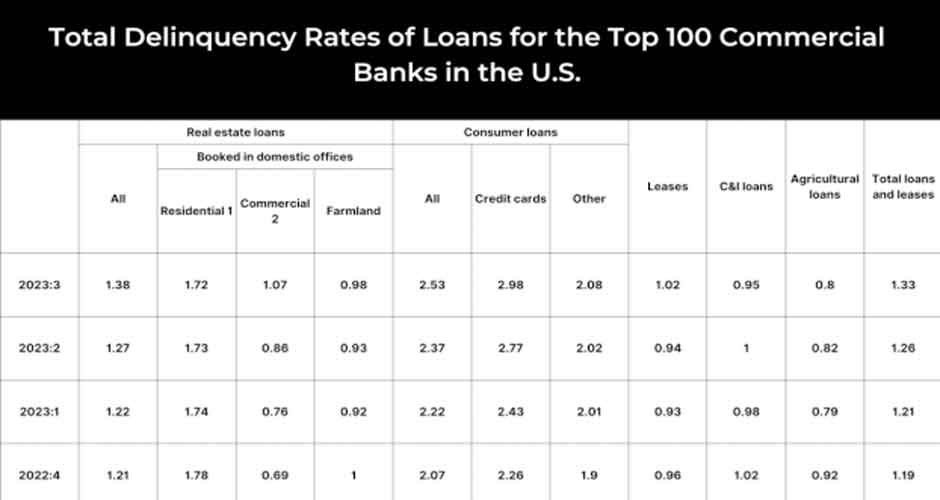
Prepaying a Personal Loan Prevents Delinquency in Loan Payment.
A. Interest savings
Prepaying a personal loan offers the potential for substantial interest savings.
The strategy involves an early reduction of the outstanding principal amount of the loan.
By decreasing the principal early, borrowers can minimize the total interest paid over the entire loan tenure. Interest is often calculated on the remaining balance, so lowering it through extra payments leads to cost savings.
Personal loan prepayment contributes to financial efficiency by optimizing interest payments.
The approach allows borrowers to redirect the saved funds toward other financial goals or investments. Making extra payments effectively lowers the interest accrual, resulting in overall cost savings for the borrower.
B. Improved Credit Score
Timely and responsible repayment, including loan prepayment, has a positive impact on an individual’s credit score. Lenders generally view borrowers who actively manage and repay debts ahead of schedule in a favorable light.
Such responsible behavior contributes to a higher credit score for the individual. A higher credit score is indicative of financial responsibility in managing credit obligations. Lenders may offer improved credit terms to borrowers with higher credit scores.
A higher credit score enhances access to better financial opportunities in the future.
Personal loan prepayment is a strategic move for individuals aiming to enhance their overall creditworthiness.
C. Financial Flexibility
Prepaying a personal loan enhances financial flexibility for borrowers. The strategy involves reducing or eliminating monthly loan obligations.
Borrowers gain the freedom to allocate the saved funds towards other financial priorities. Prepayment allows individuals to redirect funds to savings, investments, or other strategic financial goals. Increased financial flexibility serves as a valuable safety net, enabling borrowers to adapt to changing circumstances. Eliminating monthly loan payments removes the burden of fixed financial commitments for borrowers.
D. Early Debt Freedom
Personal loan prepayment offers the satisfying prospect of achieving debt freedom before the scheduled timeline. Clearing the loan ahead of maturity brings a sense of accomplishment to borrowers.
Prepayment liberates borrowers from ongoing financial commitments associated with monthly payments. The strategy provides newfound financial freedom to reallocate resources towards personal and financial goals.
Individuals can use this freedom to pursue additional education, start a business, or save for significant life events. Despite the advantages, borrowers must carefully evaluate specific loan terms, including prepayment penalties or restrictions imposed by the lender. Individual financial circumstances and goals play a crucial role in determining whether the benefits of prepayment outweigh potential drawbacks.
Exploration of Key Considerations and Challenges: The next section will explore key considerations and potential challenges associated with personal loan prepayment, offering a comprehensive view of borrowers contemplating this financial strategy.
Factors to Consider Before Prepaying
A. Payment charges and penalties
Before deciding to prepay a personal loan, borrowers must thoroughly review the terms and conditions set by their lending institution. Some lenders impose prepayment charges or penalties to compensate for the interest income they would have earned over the entire loan tenure. Understanding the specific charges and conditions associated with prepayment is crucial for making an informed decision. While some loans may have minimal or no prepayment penalties, others could significantly offset the potential interest savings, making it essential for borrowers to weigh the costs against the benefits.
B. Analyzing the impact on credit score
While personal loan prepayment can positively influence a credit score in the long run, borrowers should consider the short-term impact on their credit profile. Closing a loan account might lead to a temporary dip in the credit score, as credit scoring models also consider the length and variety of a borrower’s credit history. However, this impact is usually minimal and transient. Borrowers should assess their overall credit health and financial goals to determine whether the temporary credit score adjustment aligns with their broader financial strategy.
C. Opportunity cost of funds
Another critical factor to consider before prepaying a personal loan is the opportunity cost of the funds used for prepayment. If the funds allocated for prepayment could be invested elsewhere at a higher rate of return, borrowers may want to evaluate whether the potential investment gains outweigh the interest savings from loan prepayment. Conducting a thorough cost-benefit analysis helps borrowers make a well-informed decision based on their financial objectives, risk tolerance, and investment opportunities.
Considering these factors ensures that borrowers approach personal loan prepayment with a clear understanding of the potential benefits and drawbacks. While the advantages of interest savings, credit score improvement, and financial flexibility are enticing, it’s essential to navigate the nuances of prepayment charges and evaluate the broader financial landscape. In the final section of this article, we will summarize the key takeaways and guide making a sound decision regarding personal loan prepayment.
How to Prepay Your Loan
A. Contacting the lender
The first step towards prepaying your loan involves reaching out to your lender. Contact the customer service or loan servicing department to inquire about the specific procedures and requirements for loan prepayment. Lenders often have dedicated channels, such as phone lines, online portals, or in-person visits, to assist borrowers in navigating the prepayment process. During this interaction, it’s crucial to gather information about any potential prepayment charges, penalties, or conditions that may apply to your loan.
B. Understanding the prepayment process
Once in contact with the lender, seek a comprehensive understanding of the prepayment process. Lenders typically provide a set of guidelines and documentation requirements that borrowers must fulfill to initiate the prepayment. This may include submitting a formal request, completing specific forms, or providing additional information for verification purposes. Take note of any timelines, deadlines, or processing durations involved in the prepayment process to ensure a smooth and timely execution.
C. Making the prepayment
After gaining clarity on the prepayment process, borrowers can proceed with making the prepayment. This often involves transferring the funds directly to the lender using the specified payment methods. Lenders may offer various payment options, including online transfers, checks, or direct debits. It’s essential to confirm the exact amount to be prepaid, ensuring that it aligns with the outstanding principal and any applicable charges. Retain proof of the prepayment transaction for future reference and verification.
Additionally, for borrowers considering partial prepayment, understanding any limitations or conditions imposed by the lender is crucial. Some lenders may have restrictions on the frequency or amount of partial prepayments, so it’s advisable to clarify these details during communication with the lender.
By following these steps and maintaining open communication with the lender, borrowers can navigate the personal loan prepayment process effectively. As prepayment involves financial transactions and contractual agreements, attention to detail and adherence to the lender’s guidelines are paramount. In the concluding section of this article, we will recap the key points discussed and provide a summary to assist borrowers in making informed decisions about prepaying their loans.
Risks and Considerations
A. Hidden Charges
While the concept of personal loan prepayment is often associated with potential cost savings, borrowers should be vigilant about hidden charges that may accompany the process. Some prepay loan agreements entail additional fees to make up profit from interest.
Thoroughly reviewing the loan agreement and engaging in transparent communication with the lender can help uncover any hidden charges, ensuring that borrowers make well-informed decisions about prepayment. This then creates a harmonious relationship that benefits both parties.
B. Impact on Tax Benefits
Personal loans, especially those taken for specific purposes like education or home improvement, may offer tax benefits on the interest paid. Prepaying the loan might result in the reduction of eligible interest payments, potentially affecting the tax benefits associated with the loan. Borrowers should assess the implications on their tax liabilities and consult with financial advisors or tax professionals to understand how prepayment may impact their individual tax situations.
C. Loan Restructuring Options
Exploring Alternative Options: Before committing to personal loan prepayment, borrowers should explore alternative options provided by lenders for restructuring the loan.
Flexibility in Loan Tenure: Some lenders offer flexibility by allowing modifications to the loan tenure.
Adjusting EMI Amounts: Lenders may provide the option to adjust Equated Monthly Installment (EMI) amounts to better suit the borrower’s financial circumstances.
Other Restructuring Solutions: Beyond tenure and EMI adjustments, lenders might offer additional restructuring solutions.
Alignment with Financial Circumstances: These restructuring options aim to better align the loan terms with the borrower’s financial circumstances.
Comparison with Prepayment Benefits: Comparing the potential benefits of prepayment against available restructuring options is essential.
Balanced Decision-Making: While the advantages of interest savings and early debt freedom are compelling, a comprehensive assessment of potential drawbacks ensures a balanced decision-making process.
The goal is to enable borrowers to choose the most suitable strategy for managing their loans without incurring unnecessary costs or sacrificing valuable benefits. Understanding the risks and considerations associated with personal loan prepayment is crucial for borrowers.
Final Takeaway
Ultimately, the choice to prepay a personal loan depends on individual circumstances, financial objectives, and preferences. By weighing the benefits against the risks and considering the specific terms of their loan agreement, borrowers can make informed decisions that align with their overall financial well-being.
As with any significant financial decision, it is advisable to consult with financial advisors or professionals who can provide personalized guidance based on your unique situation. Armed with a comprehensive understanding of personal loan prepayment, borrowers can navigate the financial landscape with confidence and work toward achieving their long-term financial goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can I still avail of tax benefits if I prepay my loan?
Prepaying a personal loan may affect the tax benefits associated with the interest paid on the loan. Consult with tax professionals or financial advisors to understand the specific implications of your tax liabilities.
How do I initiate the personal loan prepayment process?
Contact your lender to initiate the prepayment process. Discuss the specific procedures, documentation requirements, and potential charges associated with prepayment. Once you have a clear understanding, follow the lender’s guidelines to make the prepayment.
Are there alternatives to prepayment, such as loan restructuring?
Some lenders offer loan restructuring options, allowing borrowers to modify the loan tenure or adjust EMI amounts. Before prepaying, explore these alternatives to ensure that prepayment aligns with your financial objectives.












Comments