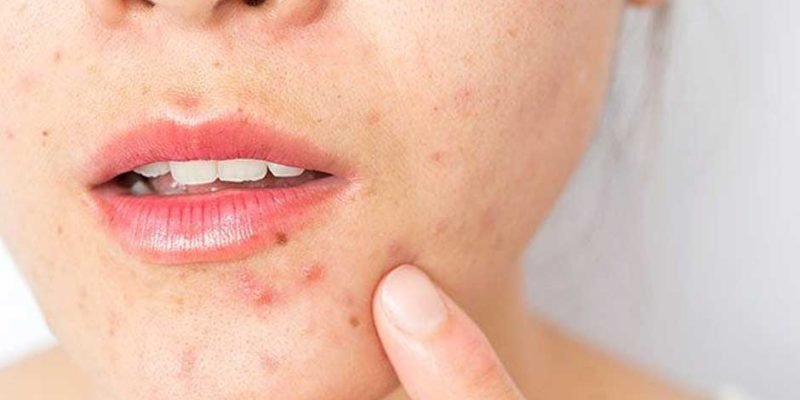
Acne is a common skin condition that affects the hair follicles and oil glands of the skin. It typically occurs during puberty when hormonal changes cause an increase in oil production. However, it can also affect people of all ages, including adults.
Acne is characterized by the presence of various types of lesions on the skin, including:
Comedones: Non-inflammatory lesions that can be open (blackheads) or closed (whiteheads). They occur when hair follicles become clogged with oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria.
Papules: Small, raised, red bumps on the skin that are often tender to touch. They result from inflammation and infection of the hair follicles.
Pustules: Similar to papules, but with a visible white or yellowish center filled with pus.
Nodules: Large, solid, painful lumps beneath the surface of the skin. They develop deeper within the skin and can be quite severe and persistent.
Cysts: Deep, painful, pus-filled lesions that can cause scarring. Cysts are the most severe form of acne and require medical attention.
While hormonal changes and excessive oil production are key factors in the development of acne, several other factors can contribute to or worsen the condition, including:
Genetics: Acne tends to run in families, suggesting a genetic predisposition.
Hormonal Fluctuations: Hormonal changes during puberty, menstrual cycles, pregnancy, or hormonal disorders can trigger or exacerbate acne.
Bacteria: Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) bacteria reside on the skin and can contribute to acne when they multiply excessively within clogged pores.
Inflammation: Inflammatory responses to bacterial growth and clogged pores can cause redness, swelling, and pain associated with acne lesions.
Certain Medications: Some medications, such as corticosteroids, androgens, or lithium, can contribute to acne development.
Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain pollutants, humid climates, and heavy sweating can worsen acne.
Cosmetics and Skincare Products: Certain products that are comedogenic (pore-clogging) or irritate the skin can contribute to acne formation.
What is the cause of acne? While acne can be frustrating, various treatment options are available. Mild cases can often be managed with over-the-counter products containing ingredients like benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid. More severe or persistent acne may require prescription medications, such as topical retinoids, antibiotics, or hormonal therapies.
A holistic dermatologist can provide tailored treatment plans based on the severity and individual needs of each person. The main cause of acne is believed to be a combination of factors, including:
Excess Sebum Production: Sebaceous glands in the skin produce an oily substance called sebum, which helps lubricate the skin. However, in some individuals, these glands may produce excessive sebum, leading to clogged pores.
Clogged Hair Follicles: When excess sebum mixes with dead skin cells and other impurities, it can clog the hair follicles or pores. This creates an environment favorable for the growth of bacteria.
Bacterial Growth: Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) is a type of bacteria that naturally resides on the skin. When hair follicles become clogged, it can multiply in the clogged pores and contribute to the development of acne. The bacteria trigger an immune response, leading to inflammation.
Inflammation: The presence of bacteria and the immune response triggered by their presence can cause inflammation within the clogged pores. Inflammation leads to redness, swelling, and the formation of acne lesions.
Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during puberty, can contribute to the development of acne. Increased androgen production stimulates the sebaceous glands, leading to increased sebum production. Hormonal changes can also affect the shedding of skin cells, making them more prone to clogging the pores.
Genetics: Acne can run in families, suggesting a genetic predisposition to the condition. If your parents or siblings had acne, you may have an increased likelihood of experiencing it as well.
So, what is the cause of acne? Several other factors can contribute to the development of acne or exacerbate existing acne. These include certain medications, hormonal imbalances (such as polycystic ovary syndrome), stress, certain cosmetic products, and diet (although the impact of diet on acne is still under study and individual responses may vary).
It’s important to note that the specific causes of acne can vary among individuals, and what triggers acne in one person may not have the same effect on another. The severity and persistence of acne can also vary, ranging from mild to severe forms such as cystic acne. If you are experiencing persistent or severe acne, it is advisable to consult a dermatologist who can provide appropriate diagnosis and treatment options.
A holistic dermatologist is a dermatologist who approaches skin health and treatment from a holistic perspective, taking into consideration the interconnectedness of the body, mind, and lifestyle factors that can influence skin conditions. They combine traditional dermatology practices with integrative and natural approaches to promote overall well-being and address skin concerns.
Holistic dermatologists often consider various factors that can contribute to skin issues, including diet, stress, and sleep patterns, environmental exposures, emotional well-being, and the use of skincare products. They focus on identifying and addressing the root causes of skin conditions rather than simply treating the symptoms.












Comments